Group Captain Shubhanshu Shukla, an Indian astronaut, embarked on his historic flight to the International Space Station (ISS) under the Axiom-4 (Ax-4) mission on June 25, 2025. This mission is a moment of pride for India, marking the return of an Indian to space after 41 years. Shubhanshu is poised to become the first Indian on the ISS.
The SpaceX Dragon spacecraft, mounted atop a Falcon-9 rocket, lifted off on June 25 at 12:01 PM IST from NASA's Kennedy Space Center, Florida. The spacecraft is scheduled to dock with the ISS on June 26, 2025, at 4:30 PM IST.
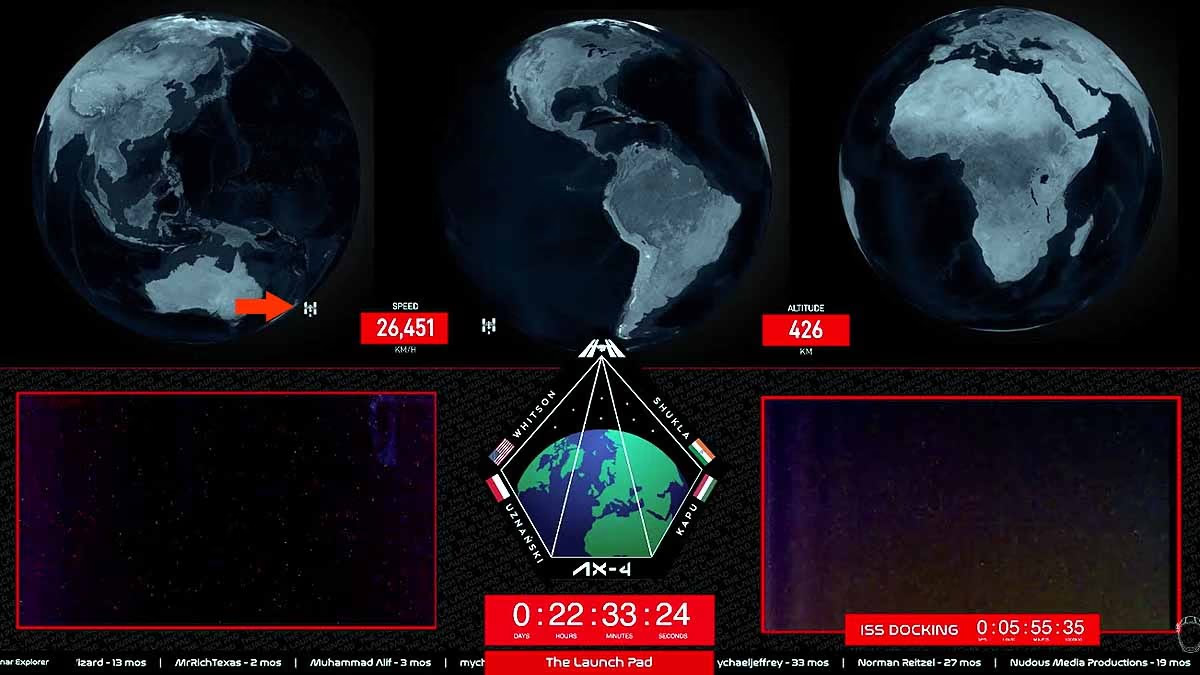
Space Journey's Current Status
As of 10:40 AM on June 26, 2025, the SpaceX Dragon spacecraft is midway through its 28-hour journey, rapidly approaching the ISS. It orbits Earth at a speed of 7.8 km/s (28,000 km/h), cruising at an altitude of about 418 km in low Earth orbit, readying for dock.
Docking Time
: The mission targets an automatic docking with the ISS's Harmony module on June 26, 2025, at 4:30 PM IST. Shubhanshu, as the mission pilot, will oversee the spacecraft's speed, orbit, and systems.
The docking of the Dragon capsule with the ISS is a complex and precise operation, occurring 12-24 hours post-launch, fully automated yet closely monitored by Shubhanshu, who may switch to manual control if necessary. The docking process unfolds as follows...
Rendezvous
To sync with the ISS orbit, the Dragon spacecraft adjusts its speed and direction with a 90-second engine firing, beginning its journey 400 meters below and 7 km behind the ISS. It navigates through multiple waypoints, where SpaceX and NASA ground controllers conduct system checks.
Close Approach
At 400 meters, Dragon establishes direct communication with the ISS. At 200 meters, it can safely hold its path for at least 6 hours, minimizing risks.

Source: aajtak
Final Approach
At just 20 meters away, Dragon uses laser sensors and cameras for precise alignment with the Harmony module's docking port, advancing at a few centimeters per second. Shubhanshu will monitor the spacecraft's speed, orbit, and systems (avionics, propulsion, life support), and manage manual control if emergencies arise.
Soft and Hard Capture
Soft Capture: Magnets pull the spaceship towards the docking port.
Hard Capture: Mechanical latches and hooks secure the spacecraft, forming an airtight seal.
Pre-Entry Check
Following docking, 1-2 hours of checks are conducted to verify air pressure and leakage stability. Then, the hatches of the ISS and Dragon are opened, allowing the crew to enter the ISS.