India recently conducted a milestone test of the Agni-5 missile, dubbed Mission Divyastra. In this test, the Agni-5 showcased the Multiple Independently Targetable Re-entry Vehicle (MIRV) technology, enabling it to target multiple objectives simultaneously.
The highlight of this test, however, was its astounding 90-degree turn mid-flight, a maneuver considered impossible for standard ballistic missiles. This feat underscores the technological might of the Defence Research and Development Organization (DRDO).
Read More: As 97 Tejas MK-1A Join, How Large Will India's Fighter Jet Fleet Be? Here's the Future Plan
What is Agni-5?
Agni-5 is an Intercontinental Ballistic Missile (ICBM), India's longest-range missile, spanning 5000 to 8000 kilometers. Powered by a three-stage solid-fuel system, it can reach speeds of Mach 24 (29,400 km/h).
Capable of targeting parts of northern China and certain European regions, Agni-5 is road-mobile and canisterized, meaning it can be transported via truck and launched within minutes. Weighing 50 tons, it can carry a payload of 1.5-2 tons.
The Astonishing 90-degree Turn
Common ballistic missiles follow a curved trajectory. However, Agni-5 executed a remarkable 90-degree turn during its mid-flight phase, a technical marvel. While such an acute turn usually risks structural disintegration due to g-forces and precision challenges, DRDO has defied the odds to accomplish this.
Read More: The Phased-out MiG-21 Fighter Jets, What's Next for the Jets and Pilots?
How was this Feat Achieved?
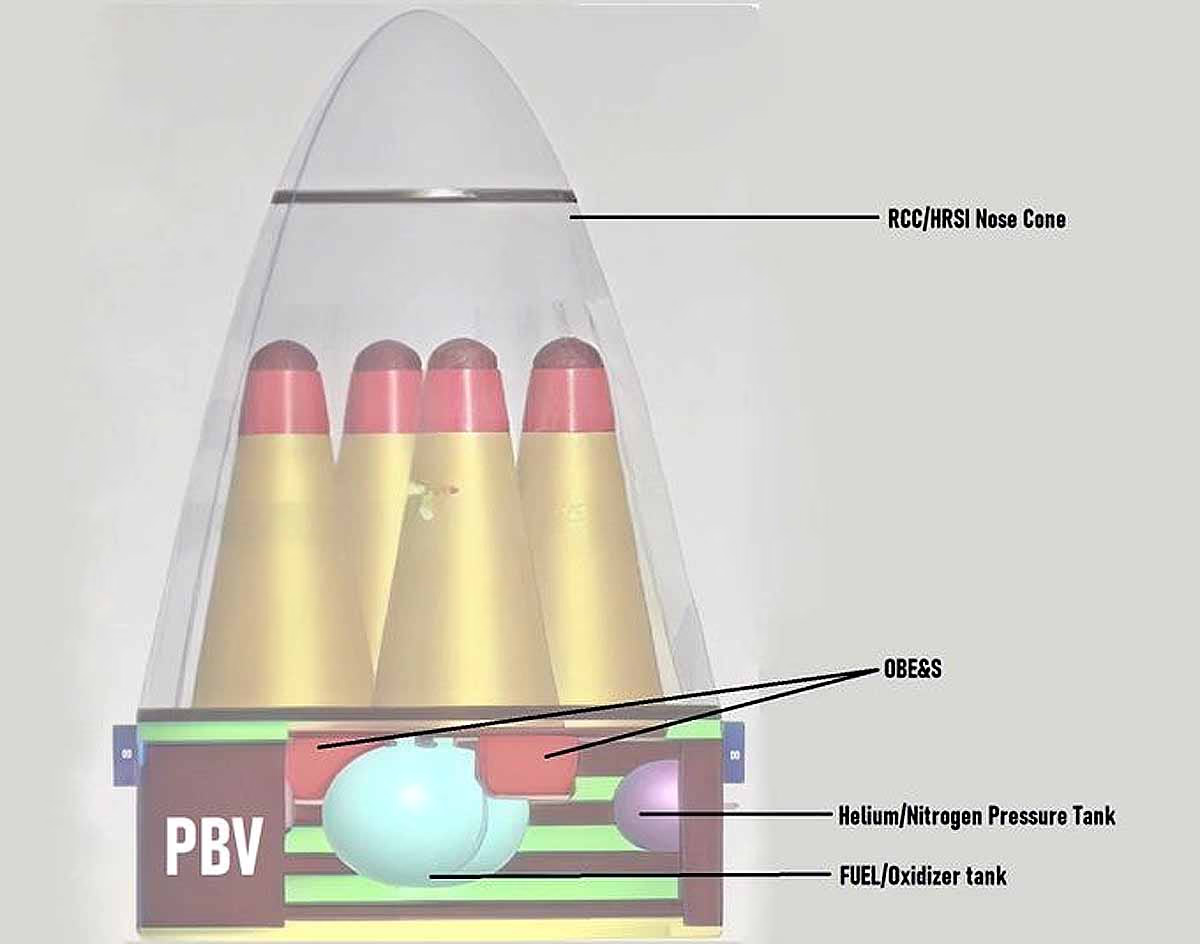
Pressure Tanks: These systems maintain pressure in propellant lines and ensure controlled tank flow, enabling precise speed and directional control.
Oxidizer Tanks: These provide thrust and agility, allowing the post-boost vehicle (PBV) or MIRV bus to deploy warheads in varied directions.
Indigenous Avionics and Sensors: The high-precision sensor package and avionics systems on Agni-5 ensured warheads reached their precise targets.
Reduced Weight: DRDO used composite materials and electro-mechanical actuators to reduce missile weight by 20%, enhancing its mobility and range.
This 90-degree turn empowers the missile to evade missile defense systems by shifting its trajectory unpredictably.
Source: aajtak
Mission Divyastra: The MIRV Magic
On March 11, 2024, from Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam Island (Odisha), the first MIRV test of Agni-5 was conducted. MIRV technology means one missile can carry multiple nuclear warheads targeting different objectives. Each warhead can weigh up to 400 kilograms. During Mission Divyastra, Agni-5 demonstrated its ability to carry four nuclear warheads.
This technology places India among the few nations (USA, Russia, China, France, and the UK) possessing MIRV missiles, enhancing India's nuclear deterrence significantly, especially against China, which already possesses MIRV missiles like DF-5B.
Read More: How E-wallets and Online Donations Funnel Terror Funds to Masood Azhar's Accounts
The MIRV Bus: How Many Warheads?
The MIRV bus is the component carrying multiple warheads, delivering them to distinct targets. Agni-5's MIRV bus can carry 4 to 5 warheads, estimated based on its size and diameter. Some experts believe it might carry 10-12 warheads, but DRDO officially confirmed 4.

Source: aajtak
Each warhead is independently guided, capable of targeting objectives up to 1,500 km.
The missile can carry decoy warheads designed to mislead enemy missile defense systems.
Carbon composites protect warheads from extreme re-entry temperatures.
Mission Divyastra's Highlights
First MIRV Test:
Conducted on March 11, 2024, this was India's first MIRV test, led by women scientists like Shankari Chandrasekharan (Project Director) and Sheela Rani (Program Director).
Indigenous Technology:
The missile utilizes indigenous avionics, precision sensors, and guidance systems, reflecting India's self-reliance vision.
Strategic Significance:
It's a stern message to neighbors like China and Pakistan, enhancing India's no-first-use policy's retaliatory prowess.
Launch System:
Launch-ready within minutes from a Transport-cum-Tilting Vehicle-5 (140 tons, 30 meters long trailer).

Source: aajtak
Why is this Achievement Significant?
Power Against China: The range and MIRV tech of Agni-5 enable it to target northern China, strengthening India's nuclear triad (aircraft, missile, and submarine).
Evading Missile Defense: The MIRV and 90-degree turn disable enemy defense systems.
Empowering Women: Women's critical roles in this mission underline India's commitment to gender equity.
Self-reliance: Based on indigenous technology, BARC developed mini nuclear warheads.
Read More: MiG-21 Bison or LCA Tejas... Debates Spark over Former Air Chief's Statements, Which Fighter Jet is Superior?
Future Plans
Agni-6:
A new MIRV-capable missile carrying 10-12 warheads with a 12,000 km range; designed, tests expected in 2024-25.
Submarine-Launch Missile (SLBM):
India to test K-series missile, deployed from submarines.
ASAT Capability:
Agni-5 also as an Anti-Satellite (ASAT) weapon, capable of downing satellites up to 800 km.
Read More: 'Operation Kahuta' - The Real Story Behind Spying in PAK that Prompted Two Web Series
Challenges and Concerns
Arms Race:
Experts warn MIRV technology may spur regional arms races, especially with China and Pakistan.
Technical Challenges:
Crafting miniaturized warheads and developing precision guidance systems are complex. Despite limited nuclear tests, India has achieved this.
Political Decisions:
Decisions concerning missile range and warhead numbers will be made by the Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS).




