In the ongoing conflicts, Israel versus Hezbollah-Iran-Hamas-Houthi, and Ukraine-Russia, missile attacks are making headlines. Alarm sirens frequently warn of impending missile strikes in Israel. Glowing lights are often seen streaking across the sky; some explode in mid-air, while others hit the ground, causing destruction and chaos.
Recently, a piece of a dismantled Iranian missile fell on a man, killing him due to the missile's weight and speed, as there was no explosion. This indicates that missiles are not entirely filled with explosives; there must be a complex system involved, like navigation, and space for weaponry storage.
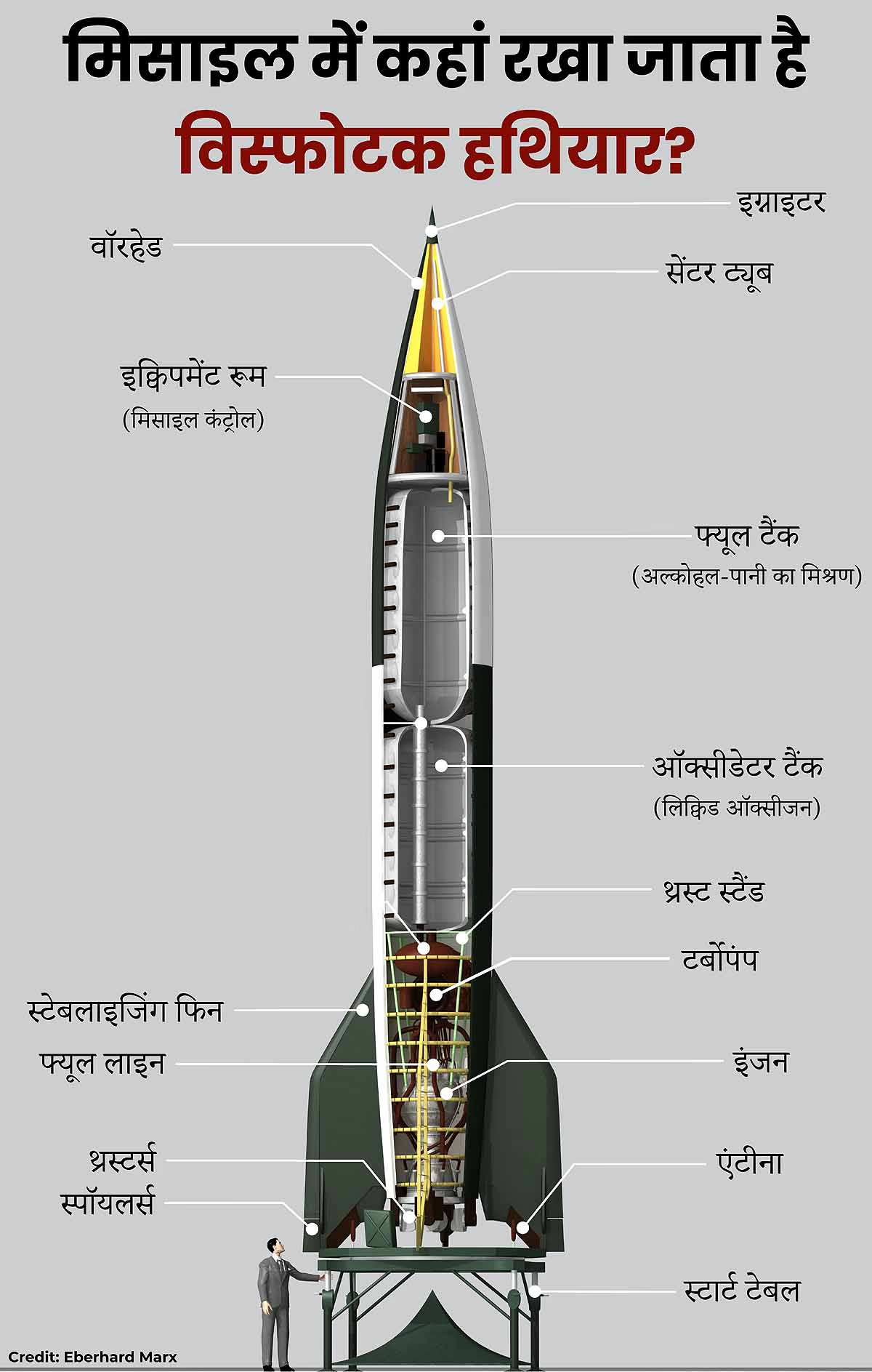
Explore the X-Ray of a Ballistic Missile Below
Source: aajtak
The Basic Internal Structure of a Ballistic Missile... common to most missiles.
Nose Cone...
The topmost section that houses the weapon, known as the warhead section, includes the payload, guidance system, and fuzing mechanism. The warhead can be conventional or nuclear, single or multiple (MIRV load). The guidance system directs the warhead to target, while the fuzing mechanism determines explosion upon impact or proximity.
Fuel Tank...
Stores the fuel, comprising propellant and oxidizer, combining to propel the missile to its target. This fuel travels to the rocket motor at the missile's base, providing thrust. It can contain solid or liquid fuel, mixing with an oxidizer.
Rocket Motor...
Provides thrust, supplying energy and altitude. Determined by fuel type—solid or liquid fuel motor.

Source: aajtak
Control Section...
Houses guidance, navigation, and control systems, ensuring accurate direction. Systems include Inertial Measurement Unit, GPS, and TERCOM for precise targeting.
Stabilizer Fin...
Ensures balance during flight.
Thrust Vectoring...
Adjusts the nozzle for directional changes, allowing trajectory adaptation.
The Four Phases of Ballistic Missile Flight...
Boost Phase...
Missile gains altitude and speed.

Source: aajtak
Post-Boost Phase...
Missile stabilizes trajectory, deploys decoys, reaching near or beyond the atmosphere.
Re-entry Phase...
Warhead re-enters atmosphere, guided by onboard systems to target.
Impact...
Direct hit on the target.
Types of Ballistic Missiles...
Ballistic missiles vary, from Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles (ICBM) with ranges over 5500 km, Intermediate Range Ballistic Missiles (IRBM) with ranges between 1000-5500 km, to Short Range Ballistic Missiles (SRBM) under 1000 km. Additionally, Submarine-Launched Ballistic Missiles (SLBM) exist.




