The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is poised to launch the SpaDeX mission on the night of December 30, 2024, at precisely 9:58. With 23 additional experimental satellites accompanying it, the launch will originate from the first launch pad of the Satish Dhawan Space Centre with the PSLV-C60 rocket, marking its 99th flight.
Source: aajtak
The POEM, or PS4-Orbital Experiment Module, represents the fourth stage of the Polar Synchronous Launch Vehicle beneath the SpaDeX satellite, enabling scientists to conduct crucial microgravity experiments in space for about three months. The module carries a total of 24 payloads, with 14 from ISRO and the Department of Science, and the remaining 10 from non-governmental organizations like colleges and startups.
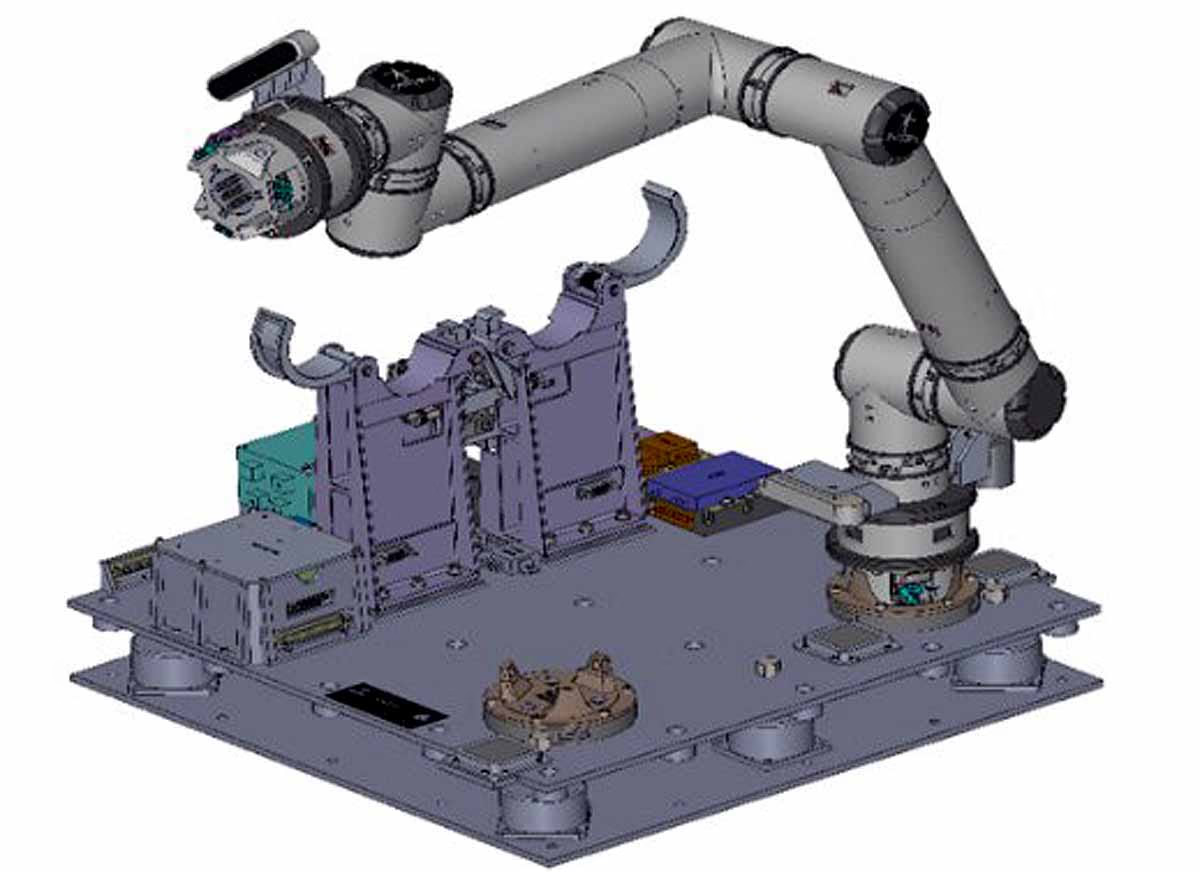
The mission also includes innovative debris capture technology: the IISU Walking Robotic Arm mimicking insect-like movements and the VSSC Debris Capture Robotic Manipulator, both aimed at addressing space debris.

Source: aajtak
This mission facilitates experiments crucial to future human activities and missions: Reaction Wheel Assembly, Multi Sensor Inertial Reference System, Lead Exempt Experimental System, MEMS-based Rate Center, Payload Common Onboard Computer, and several others.
Ten payloads are from educational institutes and startups, such as Amity University's plant gravity study, SJC Institute's amateur radio payload, RV College's microgravity study RVSat-1, and an array of innovative green propulsion systems.
An AI lab, MOI-TD from TechMe2Space in Hyderabad, is set to revolutionize space computing.
Excited to witness a rocket launch? Register now for a front-row view © Chennai and onward to Sriharikota by clicking
The SpaDeX mission includes two significant satellites, the Chaser and the Target, demonstrating docking and repositioning technologies in space. This mission will experiment with a tethered system where a robotic arm retracts the target satellite toward itself—a precursor to critical technologies for future space servicing and refueling missions, crucial for India's upcoming space advancements and the Chandrayaan-4 project.

Source: aajtak
This trajectory of innovation paves the path toward India's very own space station capabilities and supports ambitious projects like Chandrayaan-4. By integrating two separate spacecraft in orbit, ISRO is gearing up to enhance its orbital capabilities exponentially.




