Have you ever wondered why the vast area stretching from Siberia to Alaska is renowned for earthquakes and tsunamis? This region bears witness to numerous earthquakes every year, alongside occasional tsunamis. But why does this happen? Behind this phenomenon lies the story of Earth's geology and science. Let's delve into why this area has become such a zone.
Where does this region lie?
Siberia is the northern part of Russia, surrounded by the frigid Siberian tundra. Alaska is America's northernmost state, characterized by icy mountains and forests. The Arctic Ocean and Bering Sea spread out between these regions. This entire area lies on the northern edge of the Pacific Ocean, placing it in the earthquake and tsunami zone known as the Ring of Fire.
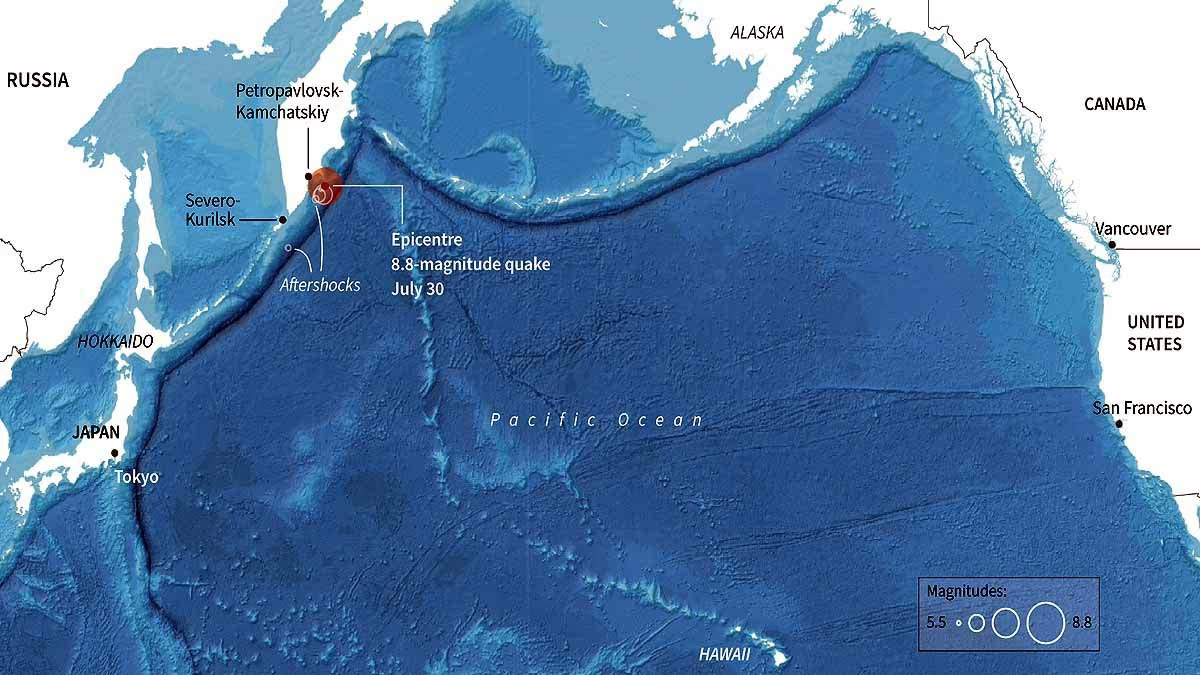
Source: aajtak
What is the Ring of Fire?
The Ring of Fire is a term used for the area encircling the Pacific Ocean like a ring, famous for its volcanoes and earthquakes. The region from Siberia to Alaska marks the northern boundary of this phenomenon, stretching around 40,000 kilometers. More than 75% of earthquakes and 80% of volcanic activities occur here. But why is this the case? Earth's surface movements are to blame.
Tectonic Plates: The Story of Earth's Rocks
Earth's surface is composed of several large segments known as tectonic plates. These plates gradually collide, slide past, or move underneath one another. The area from Siberia to Alaska lies on the boundary between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate. These plates move against each other every year at a rate of a few centimeters.
Subduction Zones: The Pacific Plate subducts beneath the North American Plate, a process known as subduction, creating immense pressure as the plates interact.
Earthquakes: When the pressure becomes too great, the plates suddenly break or shift, causing earthquakes. This activity makes the area a seismic zone due to constant tectonic shifts.
For instance,
in 1964, Alaska experienced an earthquake with a 9.2 magnitude, the second-largest quake in history.
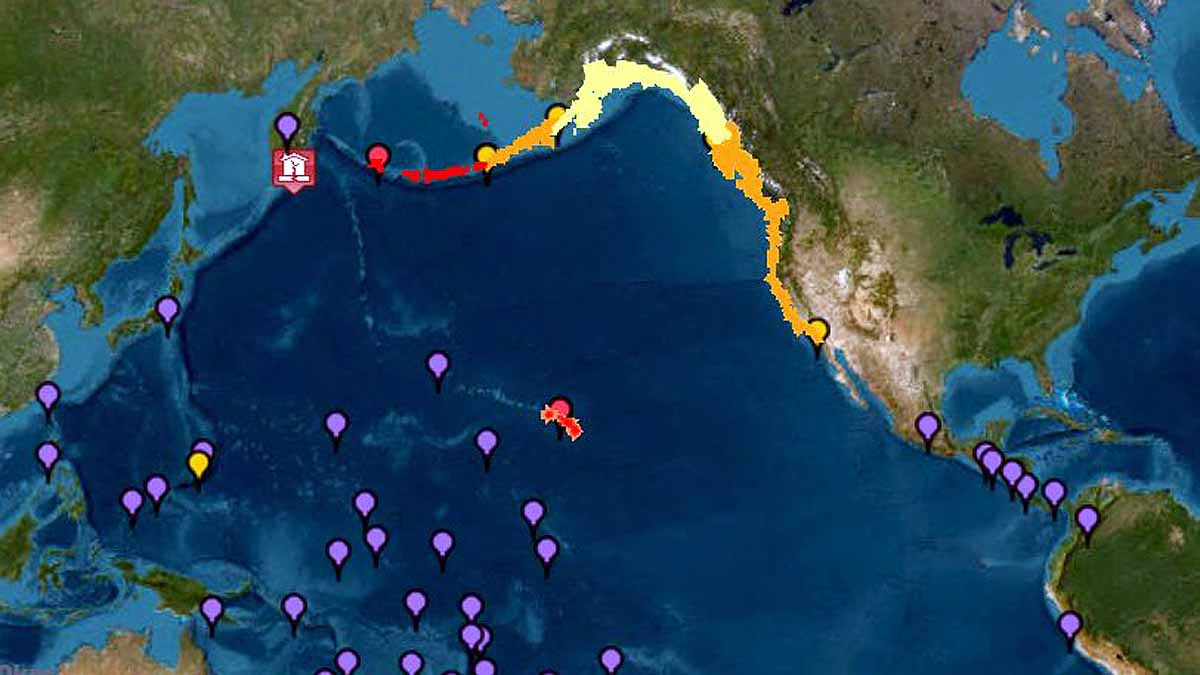
Source: aajtak
How Do Tsunamis Occur?
Following earthquakes, substantial changes in the sea floor can lead to tsunamis. The proximity of the Siberia-Alaska region to the ocean means there is a risk of tsunamis. When plates subduct, disruptions in the seabed generate massive waves that race toward coasts, potentially wreaking havoc.
Example:
In 1958, after an earthquake, Lituya Bay, Alaska, recorded the tallest tsunami ever at 524 meters high.
Why is this region special?
Geological Activity: The area experiences intense tectonic plate movement, producing earthquakes and volcanoes.
Volcanoes: Active volcanoes like Mount Redoubt and Mount Spurr in Alaska are results of plate tectonics.
Alaska’s Earthquake Record: Over 10,000 earthquakes occur annually in Alaska, though most are minor.
Siberia's Role: Siberia, particularly its eastern parts, also experiences earthquakes, contributing Russia to this seismic zone.

Source: aajtak
Scientific Insight
The movement of Earth's tectonic plates occurs at a slow pace of 2-5 centimeters yearly. This seemingly gradual motion can bring about substantial geological transformations over millions of years. Scientists highlight that the region has highly active fault lines that can trigger earthquakes and tsunamis.
Monitoring:
Advanced sensors installed by the USGS in Alaska and special monitoring systems in Russia help detect early signs of seismic activity.
Climate Change:
Global warming and melting ice are raising sea levels and pressure, potentially elevating tsunami risks.
What are the impacts?
Life: Local residents, fishers, and wildlife face threats from earthquakes and tsunamis.
Economy: Fishing and oil industries suffer damage.
Preparedness: Alaska and Russia have improved warning systems and construction designs to cope with these natural calamities.