As COVID-19 gradually spreads its tendrils once more across the nation, around 4,000 new cases were reported by Monday. Of these, approximately 1,500 were from Kerala, with states like Maharashtra and Delhi reporting nearly 500 cases each, raising fresh questions concerning the efficacy of vaccines.
The Singular Nasal Vaccine
During previous COVID-19 waves, most citizens received the Covishield vaccine from Serum Institute of India or Bharat Biotech’s Covaxin. Additionally, Russia's Sputnik V and Moderna had emergency authorizations. Post these developments, Bharat Biotech produced another nasal vaccine, known as 'iNCOVACC' or previously, BBV154, aiming to combat the virus further.
Subsequent to its December 23 approval, Bharat Biotech's nasal vaccine gained traction. It initially made its appearance in private institutions before becoming part of the government’s vaccination framework, backed by governmental funding. Yet, no further nasal vaccines emerged afterward, leaving Bharat Biotech's product as the sole contender.
Cost of Vaccination
Available on the CoWIN app, iNCOVACC is priced at ₹800 for the public, and ₹325 for government acquisition. This intranasal vaccine maintains stability between 2 to 8 degrees Celsius, ensuring its smooth distribution. Developed in collaboration with Washington University, St. Louis, its impact is profound.
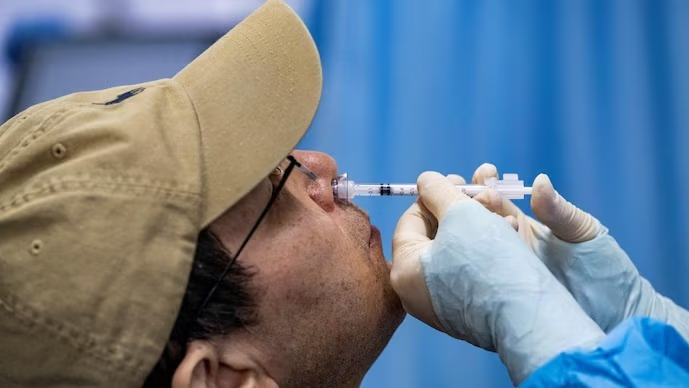
Delivered via nasal spray, iNCOVACC offers a sigh of relief as shots on the arm aren’t necessary. Former AIIMS director, Dr. Randeep Guleria, extolled its virtues, citing ease of administration and the creation of mucosal immunity, potentially halting infections at the outset. Current conditions suggest efficacy due to the limited local spread of the virus.
Is the Nasal Vaccine Safe?
A three-phase trial confirmed the effectiveness of iNCOVACC. Phase-1 trial involved 175 participants while Phase-2 engaged 200. A bifurcated Phase-3 included a primary segment of 3,100 patients receiving two doses while a secondary category of 875 experienced the booster dose. Outcomes revealed significant resistance in the upper respiratory system against COVID-19, greatly minimizing infection and transmission risks, the company asserted.